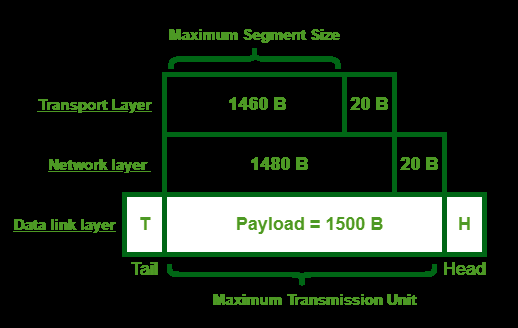
Terms:
MSS = Maximum Segment Size
MTU = Maximum Transmission Unit
CPE = Customer Premise Equipement
To get your MSS value, you simply take your chosen MTU (most likely 1500) and lower it by 40. So having an MTU size of 1500 makes you end up with a MSS size of 1460.
The MSS size gets sent in the SYN packet of a TCP communication flow.
This value gets sent by the endpoint device and is not a value that routers change by default. However sometimes you need to change it when you are working with a lower MTU link (like PPPoE which has a MTU of 1492). This is however not possible in the IPv4 world.
The solution
You can configure TCP MSS clamping on a router which you manage (like CPE). This function will set the SYN MSS flag and value to the configured value for all packets entering the router. This will resolve any problems relating to TCP MSS clamping.
Why isn’t this done on an ISP-level?
Because ISP hardware is just there to move packets from A to B and not used to manipulate that traffic anymore than needed. Because if ISP equipment had to do this, it will take things a bit ‘slower’ as all packets will first have to go from the forwarding plane to the control plane to get modified by the CPU. This takes up unneeded CPU cycles for the functioning of the ISP.